
DVI has taken over for VGA. The difference between the signals is that DVI transmitted digitally until screen. This minimizes the risk of interference that may arise along the way. In addition, the DVI is possible with higher resolution without blurring.
DVI (Digital Visual Interface) is a misleading name, since there are also analog DVI connections. DVI connector is available in different versions, depending on which signals it to handle. They called for DVI-D (digital), DVI-A (analog) and DVI-I (integrated).
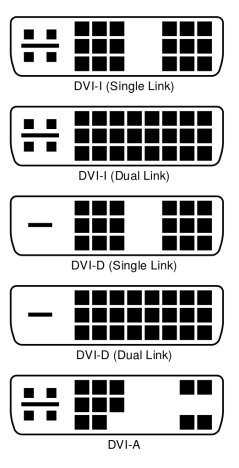
DVI female connectors on the graphics cards are usually DVI-I, since it is possible to connect a DVI-D or DVI-A cable to a DVI female. This allows the user to connect screen digital DVI-D or analog with a VGA adapter cable (DVI-A to VGA).
There are also DVI-I cables, but they should not be used to connect computer monitors directly to your computer. On computer screens sitting there namely usually DVI-D female connectors, where it is not possible to connect DVI-male connectors (the four extra pins allows the plug does not fit).
DVI-D and DVI-I is available in both single-link and dual-link. A common misconception is that the difference is whether the cable is bidirectional or not. It is really all about the maximum resolution. With single-link is the maximum resolution of 1920 x 1200 pixels at 60 Hz refresh rate. With dual-link it is possible to send an image of 2560 x 1600 pixels at the same refresh rate.
It is effortless to connect a DVI-D dual-link cable to a monitor, although it can handle only single-link. It tends namely to exist hole for these pins anyway.
DVI-D dual-link can also be used to drive game screens with a high refresh rate. DVI-D dual-link capable of handling up to 120 Hz picture refresh at 1920 x 1200 and 144 Hz at 1920 x 1080 (Full HD).

